The short history of LTE shows only five years it took from the start until the introduction. This follows the mobile a trend that can be observed in new technologies: What is now on the market, may have a million customers in near future.
Digital Mobile Radio: from GSM to LTE
The first phone last 28 years to crack 10 million mark of users. The cable television made it in 25 years to get the phone in 9 years, the wireless data transmission in 6 years, from zero to ten million customers. Faster new technologies are accepted by the mass market.
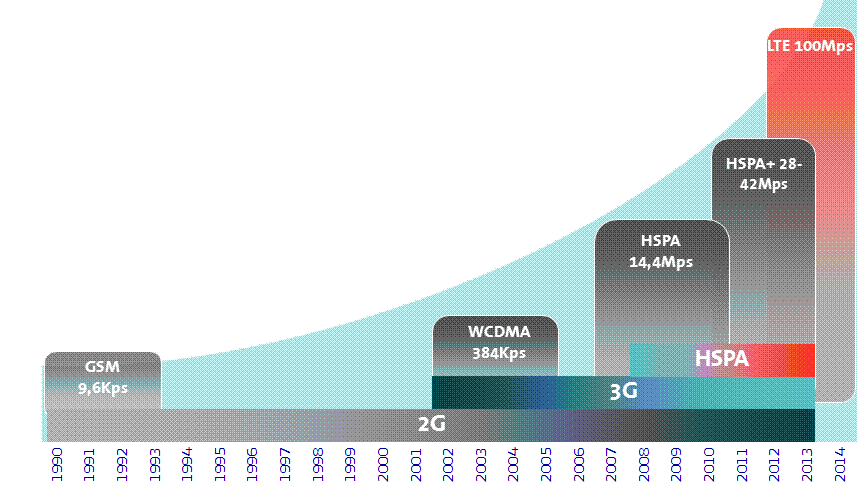
The new LTE technologies were developed as fast as any other telecommunications technology. For comparison: In 1982, the development of GSM by “Groupie Special Mobile”. It was launched by the European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations. In 1991, the first GSM network in Finland went on the air. In 1992, GSM set internationally by the market. In 1987, the UMTS Basic Research, 1992, the frequencies stipulated for 2001 launched the first commercial UMTS network, followed by the Standards for the additional technology to quickly send HSDPA(2002) and HSUPA (2005).
The UMTS technology was initially developed hesitant, we had already a digital mobile radio standard and the number of applications for faster wireless data transfer was still very manageable. Later, the networks were constructed reluctant, partly because they had to pay high license fees and the lack of money for investment, partly because the applications bring quick profits, were not in sight.
In LTE, it goes very fast
LTE everything goes much faster. For those applications that need more and more data faster by radio are finally been on UMTS market.
LTE is considered the birth of 2004, when in Toronto, held a workshop on wireless networks and LTE. About forty mobile operators were represented, to research institutes and universities. As a result, created a study on how to rapidly develop and build a fast data network, has short response times and nearly bring the performance of a wired network.
In June 2007, the standard for new mobile technology is being committed. In 2008, Ericsson unveils the Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, the first time establishes a connection between two compact LTE terminals, there will be a transfer rate of 25 mbps per second achieved. End of 2008, the Korean company LG to introduce the first-install LTE chip, it could reach peak speed at 60Mbps.
Finally, in December 2009, the first commercial LTE network in Sweden is put into operation, in late summer and fall of 2010 in Germany, the first LTE phone masts ready.
LTE: The Fastest Developed Technology
For the Global Supplier Association, a global trade association for the mobile industry, LTE is now “ the most rapidly developing technology in the history of telecommunications.”
Meanwhile, large-scale commercial LTE networks available in many countries and areas.