TP-Link M7650 was available around half a year and many people got to know this new LTE WiFi router, but regarding the performance for internet access and connection stability, many people want to know more even they may get some information from TP-Link M7650 Review. It’s better to take a test for the internet connection and find the answers. Today, we would take a test for TP-Link M7650 and see how it performs for users.
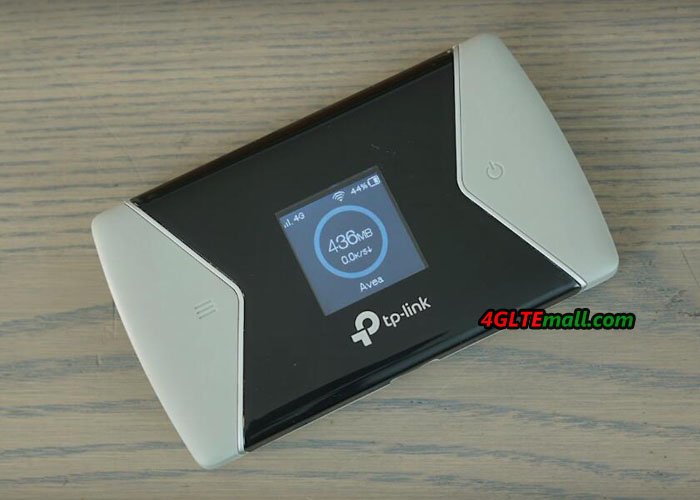

TP-Link M7650 Specifications
TP-Link M7650 is a portable LTE-A Category 11 hotspot allowing data download at speeds up to 600 Mb/s. With a 3000 mAh battery, the device can work up to 15 hours and can handle up to 32 devices. Thanks to the built-in screen with dedicated buttons, we can display current information about the router’s status and control data consumption, battery status and cellular network coverage. The manufacturer has equipped the solution with the 802.11ac standard, thanks to which the devices can communicate with the speed of 867 Mb/s.

TP-Link M7650 is not the first TP-Link 4G LTE mobile WiFi hotspot. The manufacturer has been presenting interesting “MiFi” solutions for years. The TP-Link MiFi series includes the M5350, whose successor is the LTE version TP-Link M7200. And the TP-Link M5360 3G hotspot with 5200 mAh power bank function is also in this series.

The most interesting are the M7310, M7350 and M7450 mobile WiFi hotspots, which clearly show how the mobile data transmission developed. The first two offer cellular LTE data transmission at DL 150Mbps/UL 50Mbps, while M7450 supporting LTE category 6 allows downloading at 300 Mbps and uploading at 50 Mbps. The hero of today’s test is a device supporting LTE category 11 (LTE-Advanced), and hence offering 600/50 Mbps in the mobile network.

TP-Link M7650 is based on the models M7310 and M7450. The device with dimensions of 112.5 x 66.5 x 16 mm contains a replaceable 3000 mAh battery, which, according to the manufacturer’s declaration, is sufficient for 15 hours of operation and up to 900 hours in standby mode. In predecessors (M7310 and M7350), the manufacturer TP-Link used 1800mAh and 2000 mAh batteries.
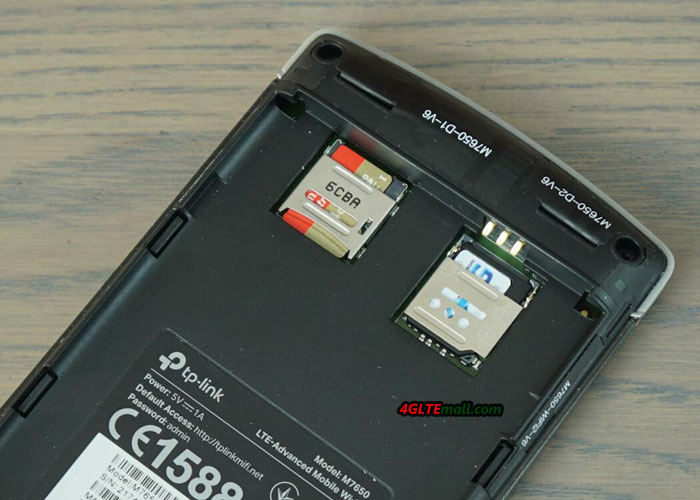

TP-Link M7650 Usage
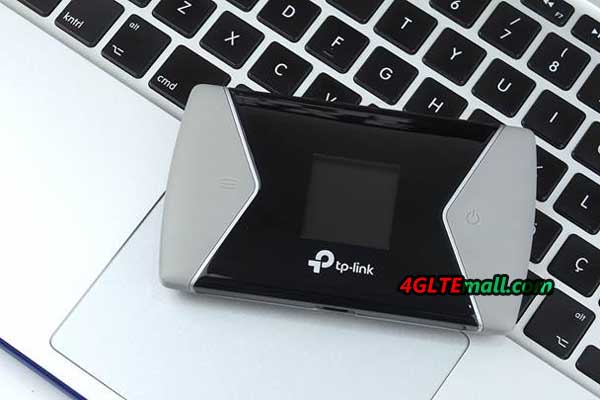
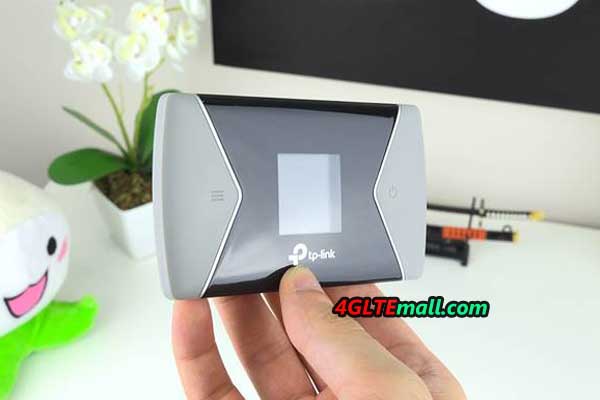
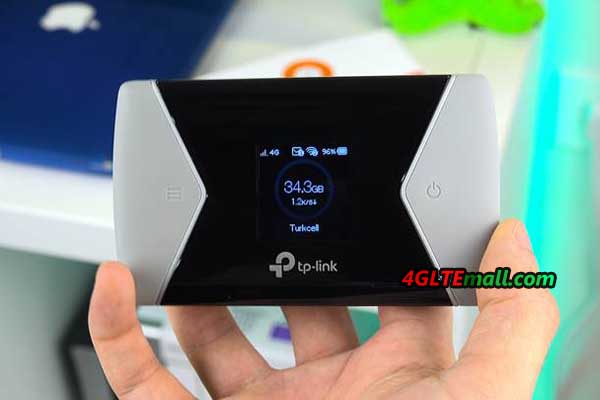
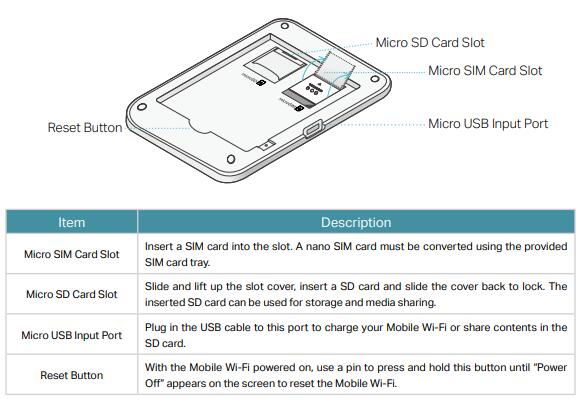
After removing the battery, there is a place for a micro SIM card and a micro SD memory card (up to 32 GB). The hotspot was made of gray, pleasant to the touch material. The front part is a black glossy element with a small (1.44 “diagonal) color LCD screen. It is not as big as Netgear models, eg AirCard 810, but the information displayed on it is very clear and the menu is transparent. On the sides of the screen there are two buttons – turning on the power supply and the hotspot menu control button. Thanks to two buttons, we can easily navigate the menu of the device and activate the most important options.
In addition to the TP-Link documentation, the set includes a nano SIM adapter – micro SIM, as well as a USB cable for charging the device or wired communication using the NDIS standard.
With the change of mobile communication technology in the TP-Link mifi, the standards of wireless communication have also changed. In the M7200 model, we had a wireless network system working at 300 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band. The M7350 has a frequency of 5 GHz. In turn, the M7450 and M7650 solutions support the latest 802.11ac standard – in the 2.4 GHz band to 300 Mbps and band 5 GHz bandwidth – 867 Mbps. Thanks to this, we can easily connect up to 32 wireless devices.

The implementation of the 802.11ac standard and operating speed in the 5 GHz band with 867 Mbps is dictated primarily by fast LTE-A communication. Although the TP-link M7650 supports a cellular network with a speed of up to 600 Mbps, at present it is difficult to find a widely available location in which we will be able to reach this value. More specifically, what technologies and frequencies does the M7650 support?
In the field of LTE networks:
- FDD-LTE: B1/B3/B7/B8/B20 (2100/1800/2600/900/800MHz)
- TDD-LTE: B38/B40/B41 (2600/2300/2500MHz)
And on the 3G/2G network:
- DC-HSPA+ /HSPA/UMTS: B1 / B8 (2100/900MHz)
- EDGE/GPRS/GSM: 850/900/1800/1900MHz
TP-Link M7650 Mobile WiFi Settings
To use the TP-Link M7650 MiFi, simply insert the SIM card and start it. Hotspot distributes a secured wireless network whose parameters (name and password) can be found on the inside of the battery cover. The advantage of TP-Link is that in the case of tested SIM cards: Play, Viking Mobile, Orange and T-Mobile, each of them was correctly recognized and there was no need to edit the connection parameters. This is especially important for people who are not familiar with the technical details of editing connection parameters.
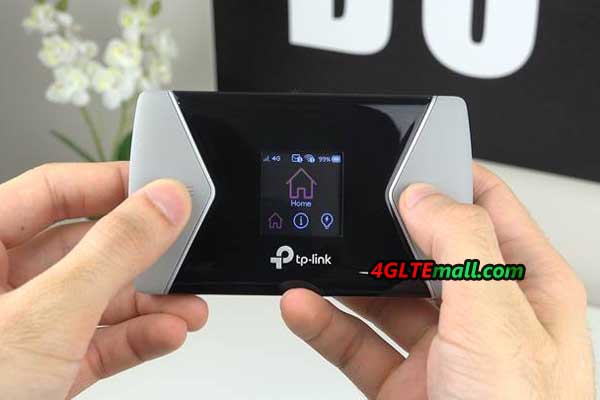
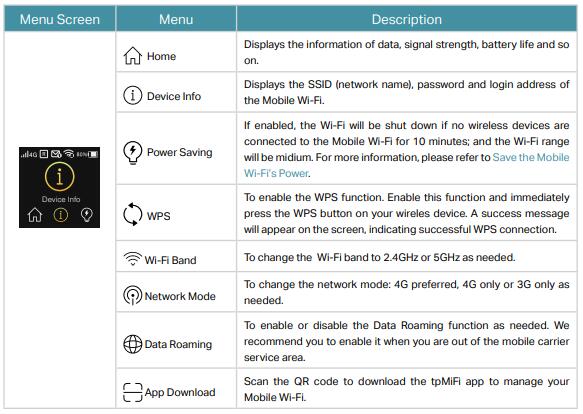
However, if we want to use the configuration options, we have three options. The first one is the LCD screen mentioned. By switching the Menu button we can set or preview:
- the name of the Wi-Fi network and its password
- Enable / disable energy saving
- Activate the mechanism of connecting to the WiFi network via WPS
- Determine the frequency of WiFi networks (2.4 or 5 GHz)
- Specify the operating mode of the 3G / 4G cellular network
- Activate GSM network roaming.
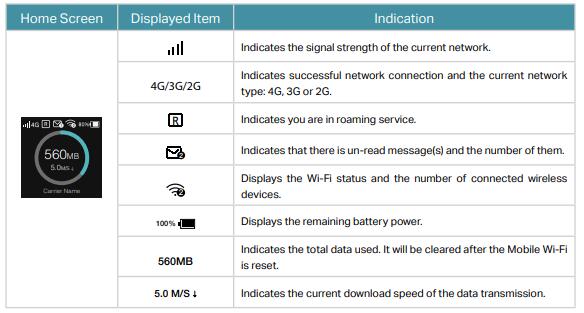
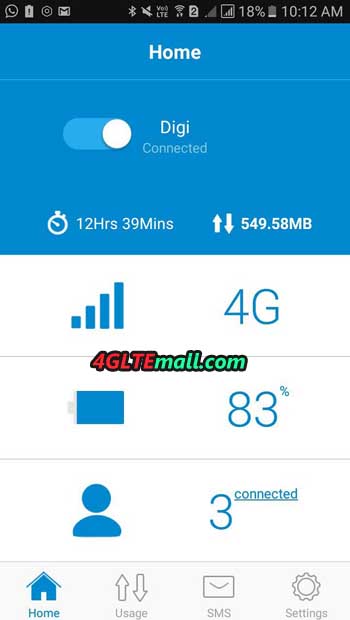
These are a few basic settings that are sufficient for an everyday mifi user. In turn, the main screen of M7650 presents the indicator and type of cellular network, enabled WiFi network, battery level as well as the name of the operator and in the central part of data consumption and download speed.
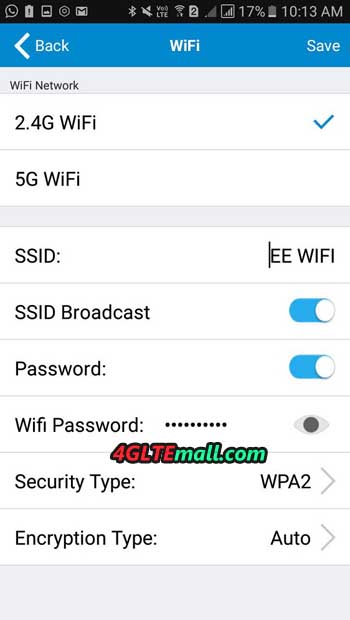
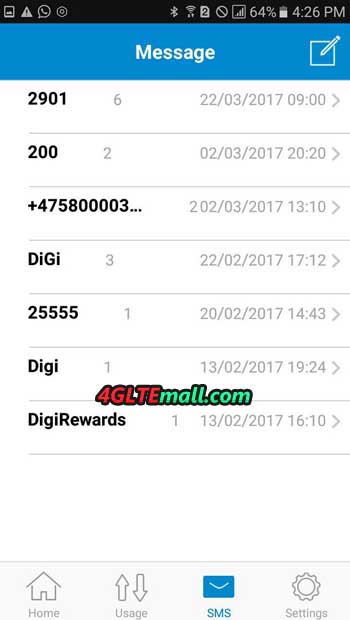
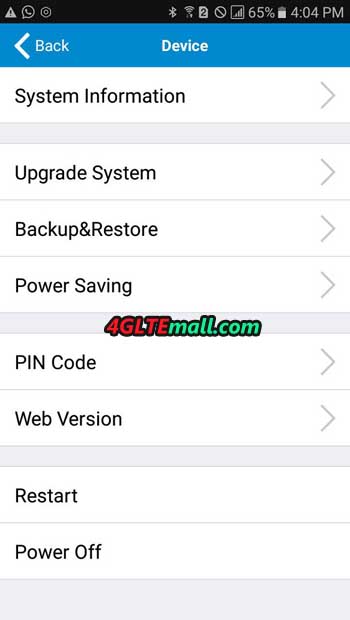
More configuration options can be found in the tpMiFi mobile application. After connecting to the Wi-Fi network provided by the hotspot, we can view the M7650 parameters:
- basic information about the device,
- wireless network options with the possibility to edit parameters,
- Mobile network options, unfortunately there is no detailed information about work in a specific LTE mode. Information about the type of 3G or 4G network remains,
- information about connected users,
- information about the status of the battery,
- SMS message panel,
- The ability to set the operating mode for the memory card – sharing via Wi-Fi or via USB. In the latter case, after connecting the M7650 to the USB port it will be visible as a flash drive,
- Additionally, in view of expenditure control and a specific data package, we can set usage limits, monthly statistics and specify a data package that is not covered by the limits (useful for “no limit” tariffs).
TP-Link M7650 mobile WiFi Hotspot Web Interfaces
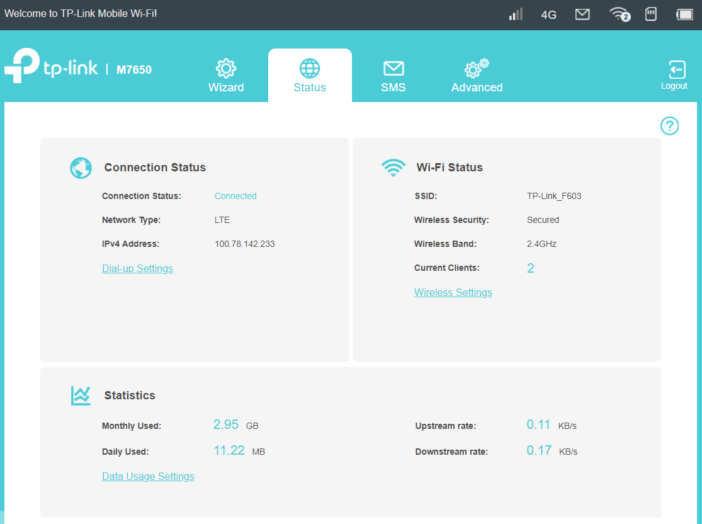
Using the web interface, we will find much more hotspot configuration parameters. The appearance of the M7650 web interface does not differ from the one we know from other TP-Link routers, such as Archer MR400. So we have a classic panel with device network status. We will also find SMS support and the TP-Link configuration wizard.
Detailed configuration options are the place in the Advanced section. Here we have a full range of possibilities:
Dial-up – tab concerning the parameters of the connection to the cellular network with the settings of the operator, the type of cellular network or the management of the PIN code
Wireless – settings responsible for the wireless network parameters.
Compared to the classic TP-Link SOHO routers, there are few settings: network name, header broadcasting, operating frequency, channel, network type, encryption and password. We also have the ability to determine whether the password and name information will be displayed on the M7650 screen. TP-Link can work on both 2.4 and 5 GHz frequencies, unfortunately not at the same time. We need to compromise and either choose a slower 2.4 GHz or have 802.11ac client devices to switch to the fast 5 GHz network. In the Wireless section, you can also view connected clients and block them access to the network, activate the WPS mechanism (PIN code, button) or edit the black list of clients
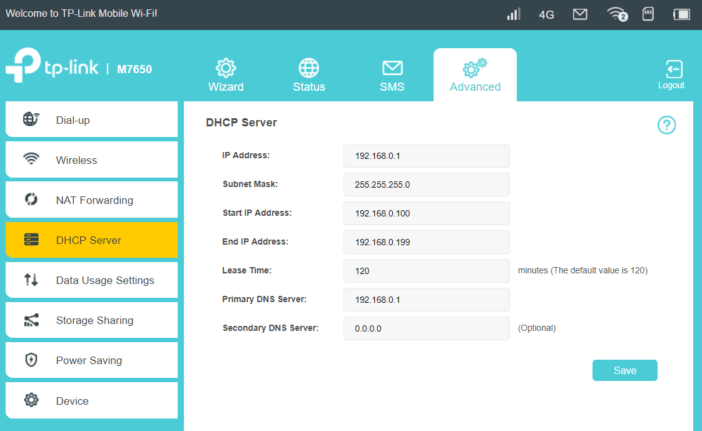
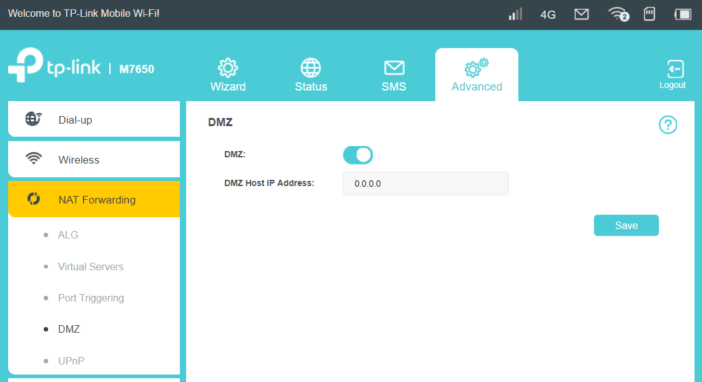
DHCP server – you probably do not need to translate too much. For a simple mechanism for dynamically assigning IP addresses. We will not find here, for example, static IP assignment based on the MAC address. It’s a pity, because in the next tab NAT Forwarding in addition to options related to ALG control, we can also set port forwarding, enable the port triggering and even assign the computer to the DMZ zone.
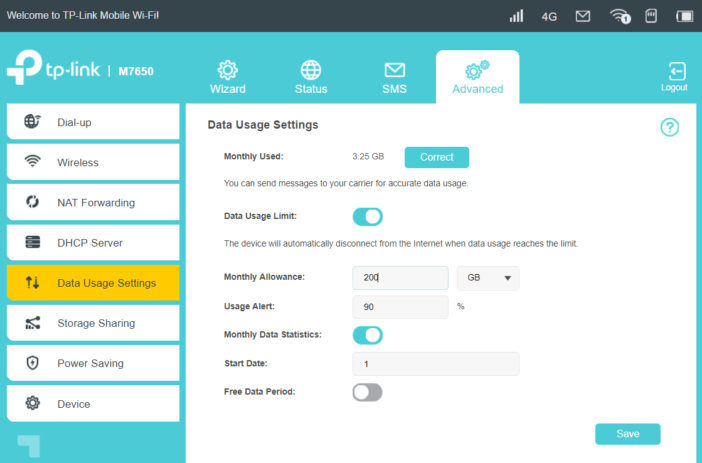
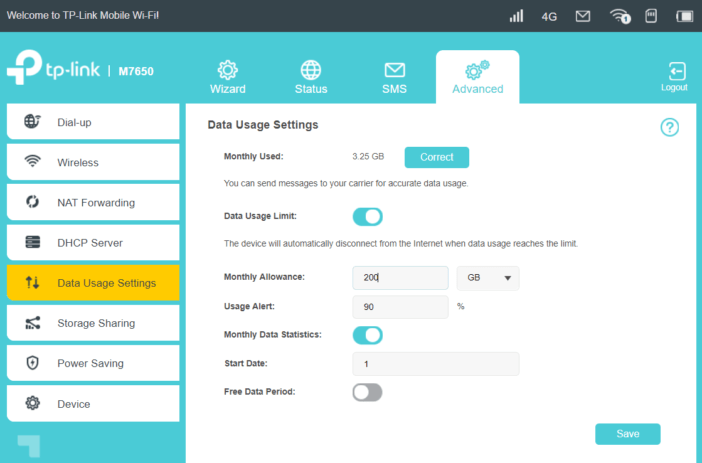
In the following sections, we will find information on data usage with the possibility to set limits and warnings when approaching the packet volume.
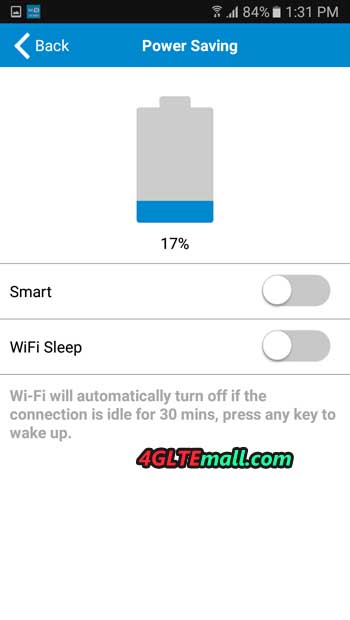
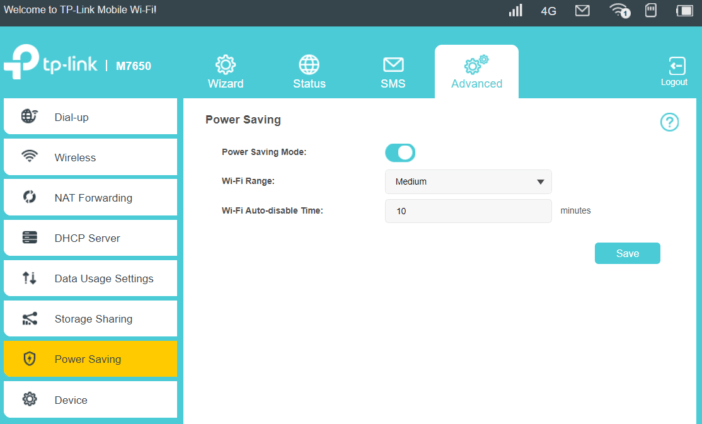
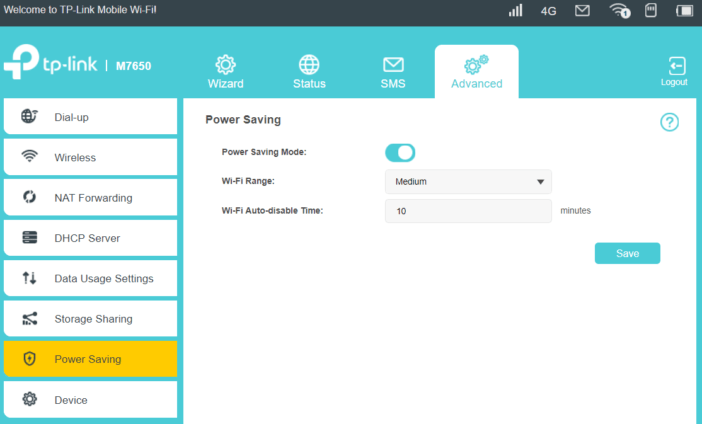
Although TP-Link implemented two radio systems and LTE-A communication, the 3000 mAh battery according to the manufacturer’s declaration should last up to 15 hours. The power saving function helps in achieving the declared working time, which in the absence of connected Wi-Fi clients disables wireless Wi-Fi after 10 minutes.
In addition, if the hotspot works in close proximity to the devices, you can also set the Wi-Fi network signal strength. During the tests, we were able to achieve the declared time of the router’s work on the battery without any problem. During intensive use by several devices, the battery was enough for about 10 hours. It’s still a great result.
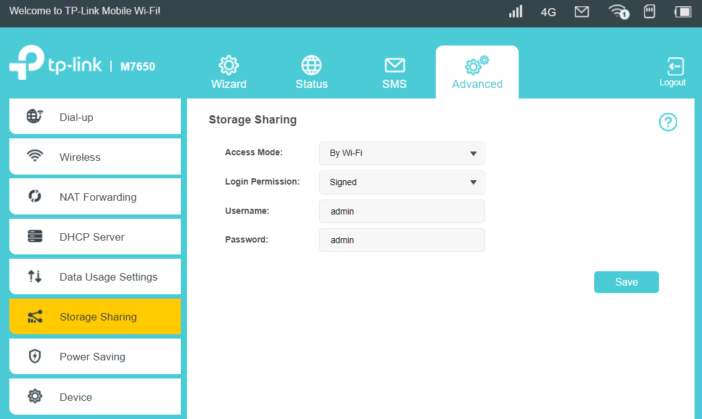
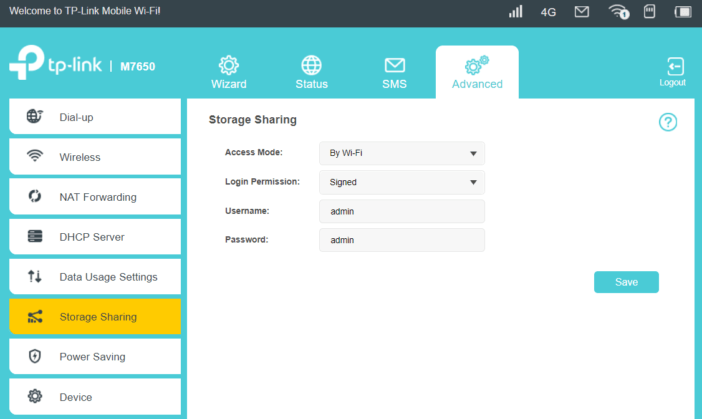
Finally, the functions associated with the memory card. You can insert a micro SD card with a capacity of up to 32 GB to the device. This is not much, but in the case of teamwork, you can use it as a place to exchange documents or store frequently used files. TP-Link implemented three possibilities of data sharing. The first one is sharing files after WiFi using the SMB protocol. Authentication takes place using the account specified in the account settings or can be anonymous. The second way is communication via FTP. In turn, the third is more individual – we can use the data by connecting the mifi to the USB port.
TP-Link M7650 Speed Tests
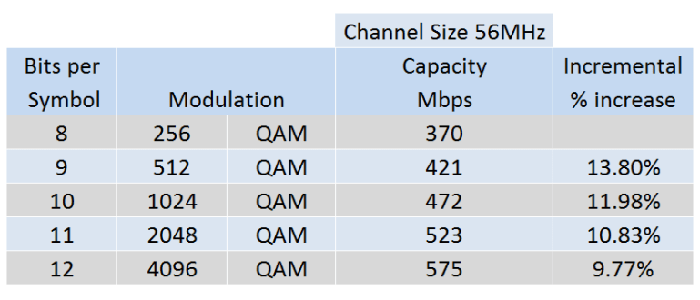
A few words of explanation at the beginning – it is possible to obtain a speed of 600 Mbps in a cellular network, but certain conditions have to be met. Well, as in Wi-Fi networks, the right number of bands and the modulation that allows LTE category 11 to obtain an aggregated frequency connection of 1800, 2100 and 2600 MHz is an important issue in the cellular network. And so for three bands with a speed of 150 Mbps, we have a total of 450 Mbps. To achieve the above mentioned 600 Mbps, it is necessary to use the 256-QAM modulation, which should improve the speed of the 64-QAM modulation connection by 30%. Similar solutions are used, among others for wireless networks for 2.4 GHz frequency, where from three streams with appropriate modulation and 256-QAM 5/6 coding, we can set up a 600 Mbps connection.
During the tests, we used cards from three operators: Viking Mobile, Orange and T-Mobile. The distance from the transmitters for individual operators was the same. We performed tests at various times of the day and night. As it turned out, the best maximum results were achieved by Viking Mobile. In the case of T-Mobile and Orange, the maximum download values ranged from 70 to 90 Mbit/s. In turn, in Viking Mobile at the same time they have already reached over 120 Mbit/s. However, it is worth remembering that Viking Mobile uses Play transmitters and in the test location we had the opportunity to use Play technology (4G LTE ULTRA).
120 Mbit/s values can be achieved when we are connected to a hotspot using USB or a 5 GHz network. In the case of the 2.4 GHz network, the connection speed in Viking Mobile dropped to around 83 Mbit/s.
Why is the communication in the 2.4 GHz network slower? First of all, the maximum available connection speed is 300 Mbit/s. This is possible thanks to two streams and 40 MHz channel. In spite of many attempts, the TP-Link M7650 stubbornly established a connection on a 20 MHz channel, which results in a long link with a maximum speed of 144.4 Mbit/s and has a direct impact on the network connection performance and indirectly on the speed of downloading and sending data to and from the Internet. In turn, if one of the devices was connected using NDIS (through USB), the communication was much more efficient. For the 2.4 GHz frequency – 82/72 Mbit/s and for the 5 GHz band: 280/239 Mbit/s.
Summary
The TP-Link M7650 mobile hotspot can be described as a very interesting yet powerful solution for home use. Long battery life will allow you to take your mifi on a trip, as well as use mobile internet at work or places where we do not have access to wireless networks. The advantage of TP-Link is the very good LTE-A network support and the possibility of remote access to the internal LAN created using the M7650. With mobile, unlimited access to the Internet, we can use the M7650 as the main source of Internet access but also for mobile entertainment and even watching video streams. It is a pity that the manufacturer has not decided to simultaneously support two bands of the wireless network. And the TP-link M7650 has not a touchscreen, which is a common feature in similar 4G LTE Mobile Hotspot.