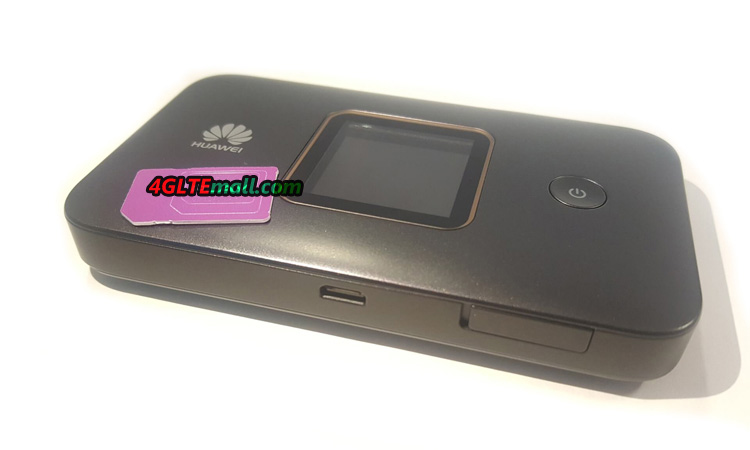
Huawei E5786 and E5785 are two popular LTE mobile routers. Many people may have them for wireless internet access. If you don’t know how to use the two mobile hotspots, below the setup guide may help you.

Simple steps to get online
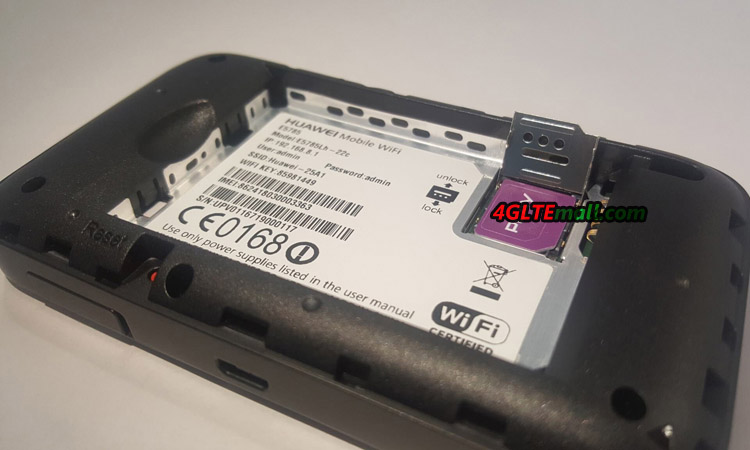
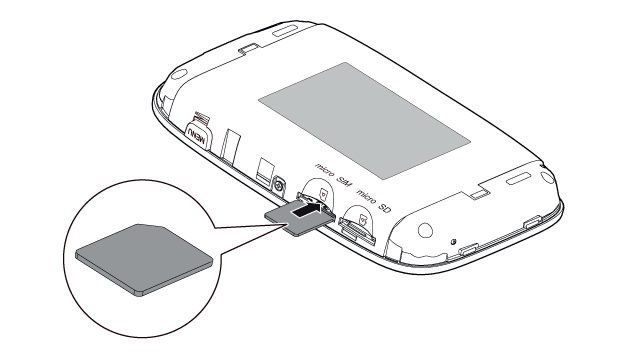
- Open the backcover and insert the SIM card:
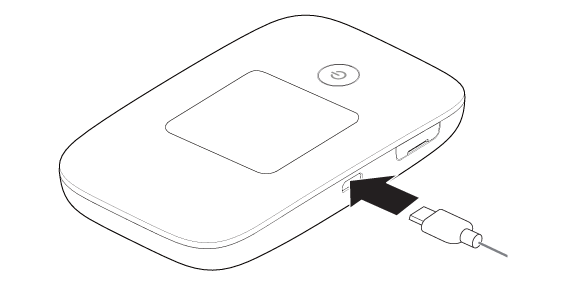
- Turn on the router and insert into the charger
- Connect a computer to the wireless network
Windows:
- Left-click the wireless network icon down at the time and date
- Locate the network that matches the network name on the bottom of the lid and press “connect”
- Enter the network password that appears on the bottom of the lid, press “connect”
Mac:
- Touch Airport, the wireless network icon
- Touch the network that matches the network name on the bottom of the lid.
- Enter the network password that appears on the bottom of the lid, press “connect”
- Open a browser and follow the wizard
Enter a URL, such as www.4gltemall.com . You will find the PIN in the letter that came with your SIM card.
If you cannot find the PIN, you need the PUK code to create a new PIN.
- You are now connected to the Internet!
Questions and answers
How do I access the router menu?
The router has its own menu, where you can change the wireless network name and network key. Here’s how to access the Huawei E5786 and Huawei E5785 router menu:
Open a new browser, such as Internet Explorer, on a computer that is connected to the router. Type 192.168.1.1 in the address bar, press Enter.
The username is admin and the password is the network key you have received (PWD / WIFI KEY)
Note: If you have changed the password yourself, enter this.
How do i know that 4G+ is available?
The router will display a “+” character behind 4G if you are in an area with 4G + coverage and user data.
How do I lock the network on 4G, 3G or 2G?
If you want to have stable network, you can lock the network on either 4G, 3G or 2G.
Here’s how to do it:
Open a new browser, such as Internet Explorer, on a computer that is connected to the router. Type 192.168.1.1 in the address bar, press Enter.
The username is admin and the password is the network key you have received (PWD / WIFI KEY)
Select Settings, then Network
Choose Auto, LTE Only, 3G Only or 2G Only from the drop-down menu under Select Network.
Press Use .
How do I restore factory settings?
If you experience trouble connecting to the Internet, it may help to reset your router.
Note, the name of the network ( SSID ) and the network key ( PWD / WIFI KEY ) can be found inside the router’s cover.
To reset the router manually:
– Open the router cover.
– Push a binder / needle into the reset hole and hold for 10 seconds.
– The router turns on and off and you can reconnect to the wireless network.
Note that after you reset your router, your network name and network password will be reset.
To restore factory settings via the menu:
– Open a new browser, such as Internet Explorer, on a computer connected to the router. Type 192.168.1.1 in the address bar, press Enter .
– The username is admin and the password is the network key you have received (PWD / WIFI KEY)
– Click Settings
– Select System Security then Factory Settings.
– Press Restore
– Press Restore again to confirm.
– The router automatically reconnects and you can reconnect. Note that after you reset the router, your network name and network password will be reset. If you have changed the login password of the router, this will also be reset.
How do I change the wireless channel?
If you have weak signal strength or trouble finding the wireless network, it may help to change the wireless channel.
To change the wireless channel, enter the router menu. The computer must be connected wirelessly to the router to access the menu.
– Open a new browser, such as Internet Explorer, on a computer connected to the router. Type 192.168.1.1 in the address bar, press Enter.
– The username is admin and the password is the network key you have received ( PWD / WIFI KEY )
– Select Settings
– Click Wi-Fi, then Advanced
– Select a channel from the drop-down menu under Frequency (Channel).
– It is recommended to choose 1, 6 or 11. Channel 11 may work better than Channel 1 at your home, so try it out. Avoid channels 12 or 13 as some network cards cannot connect to these.
– Press Use. The settings are now saved.
– If you still experience the same problem, repeat from Step 4 and try another channel that may work better on your computer.
– If you can not find your wireless network, restart your PC and your router.
Software update
The router software is automatically updated. You will be notified on the router’s screen when new software is available. If you are having trouble accessing the web, we recommend that you restore the factory settings.
How do I change Access Point Name (APN)?
- Open a web browser, such as Internet Explorer, on a computer that is connected to the router
- Type 192.168.1.1 in the address bar, press Enter
- Select Settings
- Type “admin” in the username field. The password is the same as the network key or a custom password that was selected during the initial setup of the router. The network key (WIFI KEY) can be found on a sticker on the back of the modem
- Select Profile Manager
- Touch New profile and enter the desired profile name. (this is just a description of the new profile)
- Enter the desired APN in the APN (access point name) field
- Press Save
- Restart your router.