Since 4G LTE USB modems are more and more popular in users, some users may find their 4G dongles works not as good as they first get them. They may disconnect suddenly or re-connect again, not in stable connection status. At this time, you need to update the software of the 4G LTE USB modem, just like computer, if you use too long time, it would run slow, then you need to re-store the system and you will get new speed.
Today, we would introduce how to update the software / firmware of ZTE MF820 4G LTE 100Mbps USB Modem for Windows OS and MAC OS. It includes two parts because for Windows OS and MAC OS, the software, the software is not the same.
For Windows OS Users:
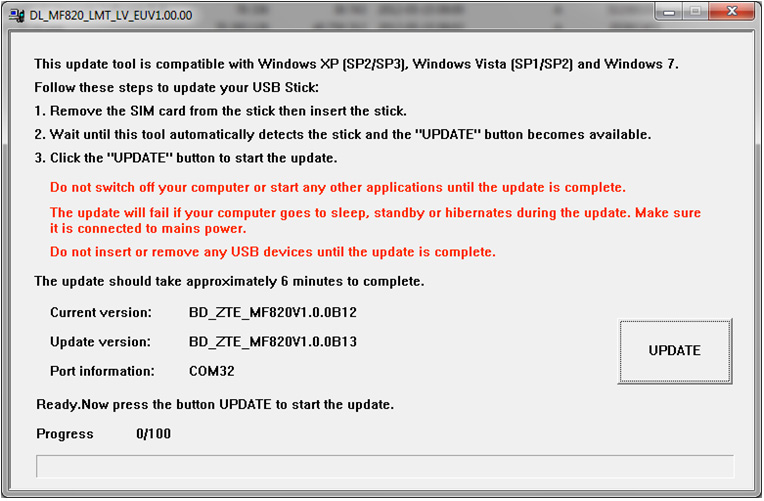
- Downloading software updates DL_MF820_LMT_LV_EUV1.00.00Setup.7z
- Unzip downloaded file.
- Unplug the modem from the computer, remove the SIM card from the modem and add a modem to your computer.
- Activates DL_MF820_LMT_LV_EUV1.00.00 file.
- Click the button Update.
- Please wait until the complete modem software upgrades. The software update may take up to 6 minutes.
- After the update, reset the previous Mobile Broadbandprogram. PCs with Windows OS Mobile Broadband software can be reset as follows: Click Start> Programs> Mobile Broadband> Uninstall.
- After the previous Mobile Broadband modem software reset is added to insert the SIM card into your computer.
- Wait until the start of the new software setup.
MAC OS X:
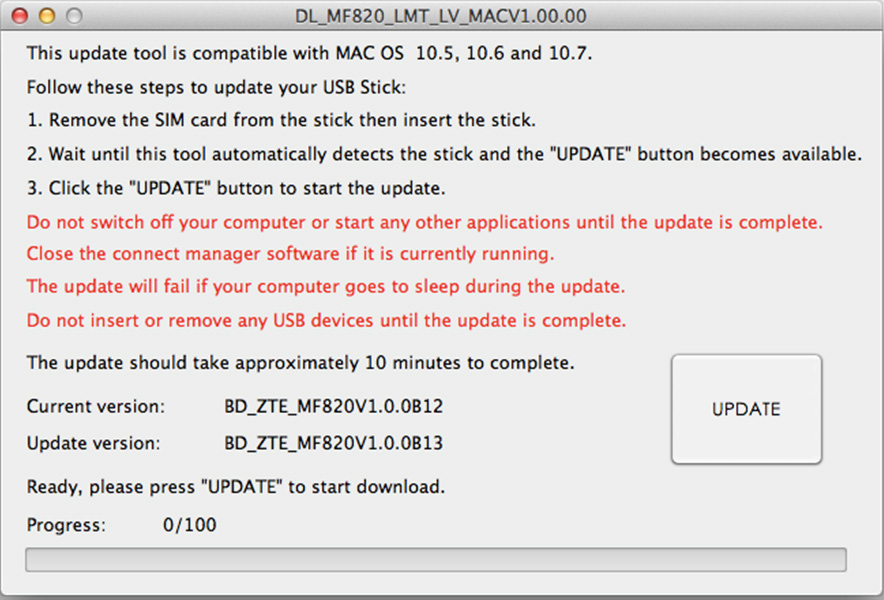
- Downloading software updates DL_MF820_LMT_LV_EUV1.00.00Setup.7z
- Unzip downloaded file.
- Unplug the modem from the computer, remove the SIM card from the modem and add a modem to your computer.
- Activates DL_MF820_LMT_LV_MACV1.00.00 file.
- Click the button Update.
- Please wait until the complete modem software upgrades. The software update may take up to 6 minutes.
- After the update reset the previous Mobile Broadband program. In Mac OS X Mobile Broadband software can be reset as follows: click Application> Mobile Broadband click on the Uninstall folder Mobile Broadband files.
- After the previous Mobile Broadband modem software reset is added to insert the SIM card into your computer. Wait until the start of the new software setup.
This is the steps to update the software of ZTE MF820 for Window and MAC operation System, hope it helps you.